Hello Readers.
Welcome to Blog,
It’s a common observation that ice floats on water. We are often told that it is so because the density of ice is lower than that of water.
But why is it that ice (a solid) has a lower density than its liquid phase- water?
The lower density of ice is explained by the presence of a special kind of bond called the hydrogen bond.
Hydrogen bond (or bonding) is a weak force of attraction, which comes about due to the dipole-dipole interaction between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom.
When a hydrogen atom is linked to a highly electronegative atom (F, O, or N) in a molecule, the electronegative atom attracts the shared pair of electrons more and so one end of the molecule becomes slightly negative while the other end becomes slightly positive. This turns a molecule into an electric dipole. The negative end of one molecule attracts the positive end of the other or to say, a weak bond is formed between them. This bond is called the hydrogen bond.
Due to H-bonding:
H2O (water) is a liquid at ordinary temperature while H2S is a gas though both O and S belong to the same group of the periodic table. It is because H2O forms hydrogen bonds. This happens due to high electronegativity and small size of oxygen (favorable condition for H-bond to form- note!)
As a result the effective molecular weight increases. (It’s like all the molecules are holding hands together and resisting to vapor away) and hence the boiling point increases. So, H2O is a liquid but H2S is not due to the large size and less electronegativity of S. (H2S molecules are alone and isolated from each other and so it is a gas)
There are many other effects of H-Bonding that one learns in multiple areas in chemistry.
So why ice has a lower density than water?
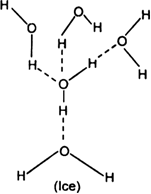
In ice, each oxygen atom is attached to four hydrogen atoms, two by covalent bonds and two by hydrogen bonds.
Due to this extensive hydrogen bonding, ice attains an “open cage-like structure” having a number of vacant spaces.
Due to this open cage-like structure with vacant spaces, the number of H2O molecules packed per ml is lower than water and thus density is lower than water.
Melting of ice results in the breaking of these hydrogen bonds. The molecules come closer to reach each other thereby increasing the number of molecules per ml. Thus, the density of water is more than that of ice. Isn’t that cool?




Comments
Post a Comment